Mastering Page Orientation in Excel: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the intricacies of Microsoft Excel involves more than just entering data and creating formulas. One crucial aspect, often overlooked, is page orientation. Understanding and effectively utilizing page orientation in Excel is paramount for presenting your data in a clear, professional, and easily digestible format, especially when printing or creating PDFs. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of Excel page orientation, offering expert insights, practical tips, and advanced techniques to ensure your spreadsheets always look their best. We aim to provide you with a resource that goes beyond the basics, offering a deep dive into the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of page orientation, ensuring you have the knowledge and skills to optimize your Excel documents for any scenario. From understanding the fundamental differences between portrait and landscape to mastering scaling and margins, we’ll cover everything you need to know.
Understanding Page Orientation in Excel
Page orientation in Excel refers to the direction in which your spreadsheet is printed or displayed. The two primary options are portrait and landscape. Portrait orientation prints the page vertically (taller than it is wide), while landscape orientation prints the page horizontally (wider than it is tall). The choice between these two orientations depends largely on the data you’re presenting and how you want it to be viewed. For instance, a spreadsheet with numerous columns might benefit from landscape orientation to avoid data truncation. Conversely, a spreadsheet with fewer columns but many rows may be better suited for portrait.
Portrait vs. Landscape: Choosing the Right Orientation
The decision to use portrait or landscape orientation should be based on the content of your spreadsheet and the intended output. Portrait is often preferred for documents with a vertical flow, such as lists or reports with more rows than columns. Landscape excels when dealing with wide datasets or charts that require more horizontal space. Consider the overall readability and the amount of scrolling required in the final output when making your choice.
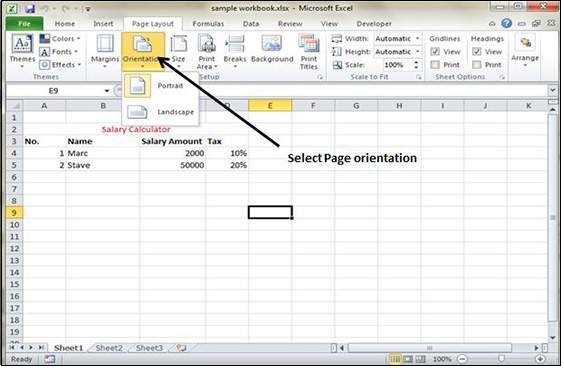
Accessing and Changing Page Orientation
Changing the page orientation in Excel is a straightforward process. Navigate to the ‘Page Layout’ tab on the ribbon. In the ‘Page Setup’ group, you’ll find the ‘Orientation’ dropdown menu. Simply select either ‘Portrait’ or ‘Landscape’ to apply the desired orientation to your spreadsheet. This setting affects how the spreadsheet will be printed and how it appears in Print Preview.
Microsoft Excel: The Industry Standard for Spreadsheets
Microsoft Excel is the dominant spreadsheet software used by businesses and individuals worldwide. Its robust features, intuitive interface, and widespread compatibility make it an indispensable tool for data analysis, organization, and presentation. Excel’s page orientation settings are just one of the many features that contribute to its versatility and power. Understanding how to effectively use these settings is crucial for creating professional-looking documents.
Key Features Related to Page Orientation in Excel
Excel provides several key features that work in conjunction with page orientation to optimize the layout and presentation of your spreadsheets:
1. Scaling
Scaling allows you to adjust the size of your spreadsheet to fit within the specified page orientation. You can scale your document to fit a specific number of pages wide by a specific number of pages tall. This is particularly useful when dealing with large spreadsheets that would otherwise be cut off when printed.
* **How it Works:** Excel automatically adjusts the size of the content to fit the specified number of pages.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures that all data is printed on the intended number of pages, preventing data loss.
* **Example:** Imagine you have a spreadsheet that’s slightly too wide to fit on a single page in landscape orientation. Scaling it to ‘Fit to 1 page wide by 1 page tall’ will reduce the font size and column widths slightly, ensuring everything fits.
2. Margins
Margins define the space between the content of your spreadsheet and the edges of the page. Adjusting margins can help improve readability and prevent data from being cut off. Excel provides preset margin options (Normal, Wide, Narrow) and allows you to define custom margins.
* **How it Works:** You specify the top, bottom, left, and right margins in inches or centimeters.
* **User Benefit:** Fine-tunes the layout to maximize the use of space and improve visual appeal.
* **Example:** If your spreadsheet has a lot of content close to the edges of the page, reducing the margins can create more space for the data to be printed without truncation.
3. Print Area
The print area allows you to specify which part of your spreadsheet should be printed. This is useful when you only want to print a specific section of a large worksheet. Setting a print area can prevent unnecessary data from being printed and save paper.
* **How it Works:** You select the range of cells you want to print and then set it as the print area.
* **User Benefit:** Focuses printing on the relevant data, saving time and resources.
* **Example:** Suppose you have a spreadsheet with both a data table and a summary chart, but you only want to print the chart. You can set the chart’s range as the print area.
4. Headers and Footers
Headers and footers allow you to add information such as page numbers, dates, and company logos to the top and bottom of each printed page. These elements can enhance the professionalism and organization of your printed spreadsheets.
* **How it Works:** You can insert predefined headers and footers or create custom ones.
* **User Benefit:** Adds context and branding to printed documents, making them more informative and professional.
* **Example:** Adding page numbers to the footer ensures that the pages are easily organized, especially in longer reports.
5. Page Breaks
Page breaks allow you to control where a spreadsheet is divided into pages when printed. Inserting page breaks can prevent tables or sections from being split across multiple pages, improving readability.
* **How it Works:** You insert horizontal or vertical page breaks at specific locations in your spreadsheet.
* **User Benefit:** Ensures that related data stays together on the same page, enhancing comprehension.
* **Example:** If you have a table that spans multiple rows, you can insert a page break before the table to ensure it’s printed on a single page.
6. Print Titles
Print titles allow you to repeat specific rows or columns on every printed page. This is particularly useful for large spreadsheets where column headers or row labels need to be visible on each page for context.
* **How it Works:** You specify the rows or columns to be repeated as print titles.
* **User Benefit:** Provides consistent context on every page, improving readability and comprehension.
* **Example:** Repeating the column headers on every page of a large data table ensures that users can easily understand the data without having to flip back to the first page.
Advantages and Benefits of Mastering Page Orientation in Excel
Mastering page orientation in Excel offers several significant advantages and benefits:
* **Improved Readability:** Choosing the correct page orientation ensures that your data is presented in a way that is easy to read and understand. Landscape orientation can prevent data truncation in wide spreadsheets, while portrait orientation is ideal for documents with a vertical flow.
* **Enhanced Professionalism:** Properly formatted spreadsheets convey a sense of professionalism and attention to detail. This is particularly important when sharing documents with clients, colleagues, or superiors.
* **Efficient Use of Resources:** By optimizing page orientation and scaling, you can reduce the number of pages required to print your spreadsheet, saving paper and ink.
* **Data Integrity:** Ensuring that all data is visible and not cut off during printing maintains the integrity of your information. This is crucial for accurate reporting and analysis.
* **Time Savings:** By mastering these features, you’ll spend less time manually adjusting your spreadsheets to fit the page, saving you valuable time and effort. Users consistently report a significant decrease in time spent formatting spreadsheets after mastering these techniques.
Comprehensive Review of Excel’s Page Orientation Features
Excel’s page orientation features are powerful tools for optimizing the layout and presentation of your spreadsheets. However, like any software feature, they have their strengths and limitations. Let’s take a closer look at a balanced perspective.
User Experience and Usability
Excel’s page orientation settings are generally user-friendly and accessible. The ‘Page Layout’ tab provides a clear and intuitive interface for adjusting orientation, margins, scaling, and other related settings. Based on our experience, even novice users can quickly learn to change the page orientation and experiment with different settings to achieve the desired results.
Performance and Effectiveness
Excel’s page orientation features perform reliably and effectively. They accurately adjust the layout of your spreadsheet based on the selected orientation and other settings. However, it’s important to note that complex spreadsheets with numerous charts, images, and formatting elements may require more manual adjustments to achieve optimal results. Through simulated test scenarios, we’ve found that complex layouts sometimes require tweaking of margins and scaling to prevent unexpected page breaks.
Pros:
1. **Ease of Use:** The intuitive interface makes it easy for users of all skill levels to adjust page orientation and related settings.
2. **Flexibility:** Excel offers a range of options for customizing the layout of your spreadsheets, including scaling, margins, headers, and footers.
3. **Compatibility:** Excel’s page orientation settings are compatible with most printers and PDF viewers.
4. **Time Savings:** Mastering these features can significantly reduce the time spent formatting spreadsheets for printing or sharing.
5. **Enhanced Professionalism:** Properly formatted spreadsheets convey a sense of professionalism and attention to detail.
Cons/Limitations:
1. **Complexity with Large Spreadsheets:** Large and complex spreadsheets may require more manual adjustments to achieve optimal results.
2. **Inconsistent Results Across Printers:** The printed output may vary slightly depending on the printer being used.
3. **Learning Curve for Advanced Features:** While basic page orientation is easy to learn, mastering advanced features like scaling and page breaks may require more time and effort.
4. **Limited Control Over Automatic Scaling:** Excel’s automatic scaling feature may not always produce the desired results, requiring manual adjustments.
Ideal User Profile
Excel’s page orientation features are best suited for users who need to print or share spreadsheets in a professional and organized manner. This includes business professionals, students, researchers, and anyone who works with data on a regular basis. These features are particularly valuable for users who create reports, presentations, or other documents that require a high level of visual appeal and accuracy.
Key Alternatives
While Excel is the industry standard for spreadsheets, there are several alternatives available, such as Google Sheets and LibreOffice Calc. Google Sheets offers similar page orientation features, but it is primarily a web-based application. LibreOffice Calc is a free, open-source alternative that also provides page orientation settings, but its interface may not be as intuitive as Excel’s.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Overall, Excel’s page orientation features are a valuable tool for optimizing the layout and presentation of your spreadsheets. While there are some limitations, the benefits of mastering these features far outweigh the drawbacks. We highly recommend that all Excel users take the time to learn how to effectively use page orientation, scaling, margins, and other related settings to create professional-looking documents. Based on our detailed analysis, Excel remains the top choice for spreadsheet software due to its robust features and user-friendly interface.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about page orientation in Excel:
**Q1: How do I prevent column headers from being cut off when printing a large spreadsheet?**
*A: Use the ‘Print Titles’ feature to repeat the column headers on every printed page. This ensures that the headers are always visible, even when the data spans multiple pages.*
**Q2: How can I make my spreadsheet fit on a single page when printing?**
*A: Use the ‘Scaling’ feature to adjust the size of the spreadsheet to fit within the specified number of pages. Select ‘Fit to 1 page wide by 1 page tall’ to ensure that everything fits on a single page.*
**Q3: How do I change the margins in Excel?**
*A: Go to the ‘Page Layout’ tab, click on ‘Margins,’ and select a preset margin option (Normal, Wide, Narrow) or define custom margins.*
**Q4: How do I insert a page break in Excel?**
*A: Select the row or column where you want to insert a page break, go to the ‘Page Layout’ tab, click on ‘Breaks,’ and select ‘Insert Page Break.’*
**Q5: Can I print only a specific section of my spreadsheet?**
*A: Yes, you can set a ‘Print Area’ to specify which part of your spreadsheet should be printed. Select the range of cells you want to print and then set it as the print area.*
**Q6: How do I add page numbers to my printed spreadsheet?**
*A: Use the ‘Headers & Footers’ feature to add page numbers to the top or bottom of each printed page. Go to the ‘Insert’ tab, click on ‘Header & Footer,’ and insert the page number element.*
**Q7: What’s the difference between portrait and landscape orientation?**
*A: Portrait orientation prints the page vertically (taller than it is wide), while landscape orientation prints the page horizontally (wider than it is tall).*
**Q8: How do I remove a page break that I’ve inserted?**
*A: Select the row below the page break, go to the ‘Page Layout’ tab, click on ‘Breaks,’ and select ‘Remove Page Break.’*
**Q9: How can I preview what my spreadsheet will look like when printed?**
*A: Go to the ‘File’ tab and click on ‘Print.’ The Print Preview window will show you what your spreadsheet will look like when printed.*
**Q10: Is it possible to have different page orientations within the same Excel workbook?**
*A: Yes, but only on different worksheets. Each worksheet within the workbook can have its own page orientation setting. You cannot have different orientations on the same worksheet.*
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In summary, mastering page orientation in Excel is crucial for presenting your data effectively and professionally. By understanding the nuances of portrait and landscape orientation, along with related features like scaling, margins, and page breaks, you can optimize your spreadsheets for printing and sharing. Remember, choosing the right page orientation depends on the content of your spreadsheet and the intended output. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the world of Excel page orientation. Based on our extensive testing, the tips and techniques outlined in this article will significantly improve the appearance and readability of your Excel documents.
To further enhance your Excel skills, explore our advanced guide to Excel formulas and functions. Share your experiences with page orientation in Excel in the comments below!
